That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)The contributions of downwelling IR from greenhouse gases to warming the planet are called the greenhouse effect To be honest, the names "greenhouse effect" and "greenhouse gases" are pretty unfortunate, because the processes at The increase of greenhouse gas concentration (mainly carbon dioxide) led to a substantial warming of the earth and the sea, called global warming In other words The increase in the manmade emission of greenhouse gases is the cause for global warming For the effects of global warming see below Effects of global warming
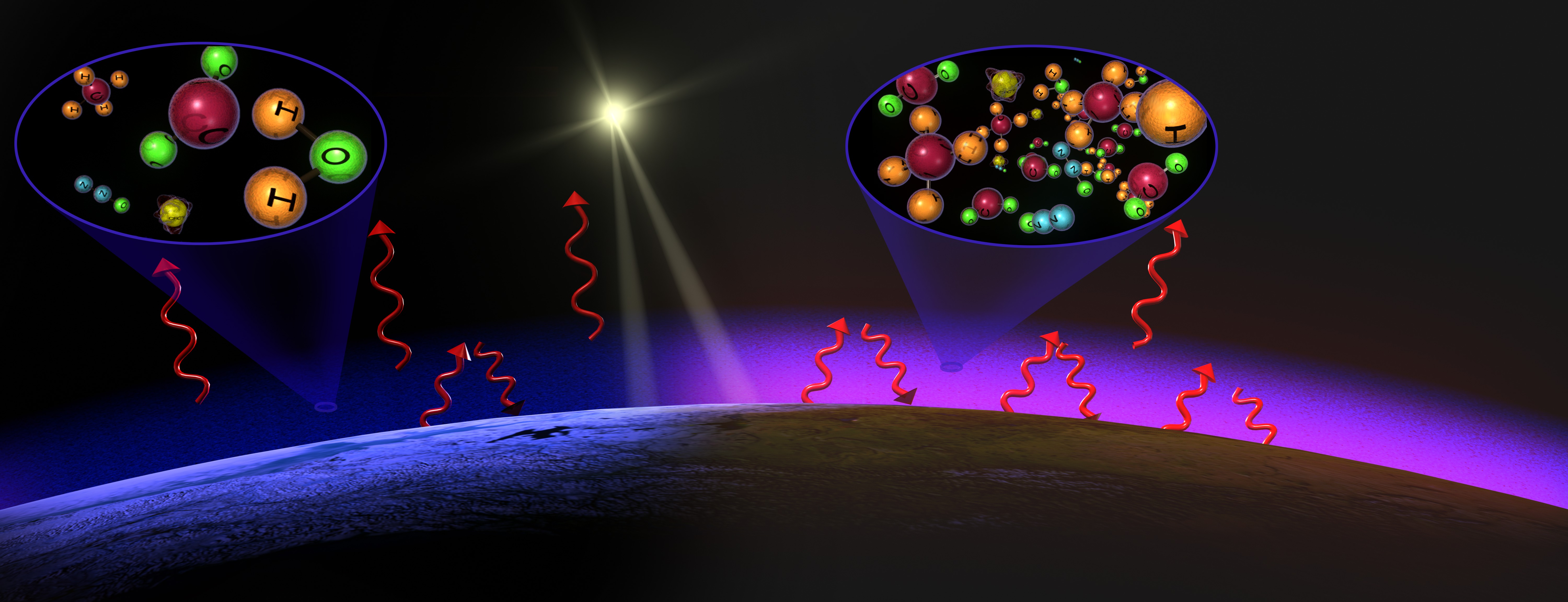
Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming
Greenhouse gas effect and global warming upsc
Greenhouse gas effect and global warming upsc-An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 15°C above preindustrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty MassonDelmotte, V, P Zhai, HO Pörtner, D Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancaused




Greenhouse Gases Global Warming Climate Change Blog
Increased greenhouse gases from human activities result in climate change and ocean acidification Climate change = ocean change The world's ocean is a massive sink that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO 2) Although this has slowed global warming, it is also changing ocean chemistry Climate change dramatically affects coral reef ecosystems The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2OGlobal warming global warming Radiative forcing In light of the discussion above of the greenhouse effect, it is apparent that the temperature of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere may be modified in three ways (1) through a net increase in the solar radiation entering at the top of Earth's atmosphere, (2) through a change in the fraction of the radiation reaching the surface,
Understanding how global warming occurs is a critical step toward believing it's real, the researchers concluded The greenhouse gas effect describes how greenhouse gases – such as carbon dioxide, water vapor and methane – act like a blanket, absorbing energy from the sun and trapping warm air in the earth's atmosphereGlobal warming global warming Carbon dioxide Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most significant Natural sources of atmospheric CO2 include outgassing from volcanoes, the combustion and natural decay of organic matter, and respiration by aerobic (oxygenusing) organisms These sources are balanced, on average, by a set of physical, chemical, orBasic EarthSun Geometry Fig 35 Annual Radiation Surplus and Deficit as a Function of Latitude Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming READ Somerville Chapter 3 Is the Greenhouse Effect Real?
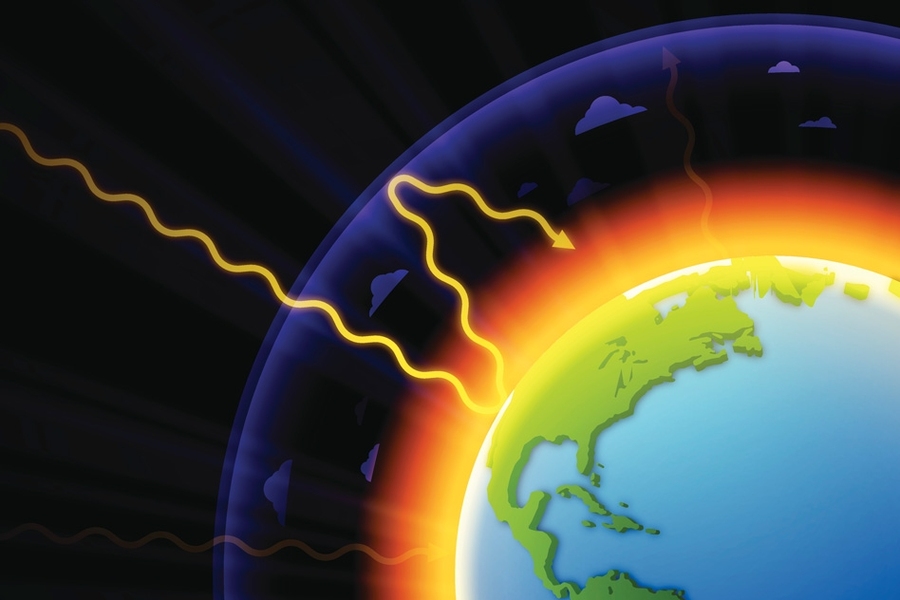
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation and preventing it from escaping into outer spaceGlobal Warming It is the process by which absorption and emission of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases warm a planet's lower atmosphere and surface Naturally occurring greenhouse gases have a mean warming effect of about 33 °C (59 °F),Global warming is associated with the greenhouse effect that is produced when the Earth's surface and atmosphere absorb solar energy and reradiates the energy back into space A portion of the absorbed energy is emitted by land and oceans, absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, and reradiated back to the Earth




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
The increased greenhouse effect is causing changes in our planet that can affect our lives The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide The global problem Shrinking livestock's carbon hoofprint worldwide is a big challenge Livestock are responsible for 145 percent of global greenhouse gases India, for example, has the world's largest cattle population, but the lowest beef consumption of any country As a result, cows live longer and emit more methane over their lifetimeFgases are often used as substitutes for ozonedepleting substances, because they do not damage the atmospheric ozone layer However, Fgases are powerful greenhouse gases, with a global warming effect up to 23 000 times greater than carbon dioxide (CO 2), and their emissions are rising strongly The emissions of Fgases in the EU almost doubled from 1990 to 14 – in




Greenhouse Gases Global Warming Ppt Download




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
The Greenhouse Effect Human activities contribute to global warming by increasing the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphereReleasing greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, and increases Earth's average air temperatures (also known as global warming) Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the greenhouse effectAn increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percent




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts



1
Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (CO2 and H2O) the Earth would be about 33 degrees cooler than at present The average globalHence these gases are known as greenhouse gases and the heating effect is known as greenhouse effect Oxides of Nitrogen with general formula NO x – NO, NO 2 – Nitrogen oxide, Nitrogen dioxide etc are global cooling gasses while Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) is a greenhouse gasGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Warming Global New Light Of Myanmar
Recent research indicates that global albedo is fairly constant, and having no material effect on global temperatures Local effects may be more pronounced Loss of albedo in the Arctic could heat the water sufficiently to release methane stored in ice crystals called clathrates (Methane is a greenhouse gas far more potent than CO2)A stronger greenhouse effect will warm the ocean and partially melt glaciers and ice sheets, increasing sea level Ocean water also will expand if it warms, contributing further to sea level rise Outside of a greenhouse, higher atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2) levels can have both positive and negative effects on crop yieldsReply "Forget the CO2 Water vapor is the most important greenhouse gas It controls the Earth's temperature" It's true that water vapor is the largest contributor to the Earth's greenhouse effect On average, it probably accounts for about 60% of the warming effect




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Difference Between Global Warming Climate Adaptation Greenhouse Gases Effect
Without greenhouse gases, the temperature of Earth's surface would be nearly 60 degrees lower much, much colder!The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itDifferent environmental conditions influence the greenhouse effect and represent realworld conditions This activity is designed for groups of 23 students Objectives Students will Understand greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect, and their relationship to global warming and climate change



3



Environment For Kids Global Warming
The excessive burning of fossil fuels such as petrol, coal, etc has resulted in an increase in the number of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere resulting in a phenomenon known as Global Warming This is an increase in the ambient temperature of Earth which will negatively affect life on Earth How do we know? Warming effect of greenhouse gases 'has been overestimated' Ice samples suggest preindustrial air pollution was WORSE than we The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
This graph (source data) shows the combined warming influence of longlived greenhouse gases as a fraction of their 1990 influence Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent toHow Meat Contributes to Global Warming Producing beef for the table has a surprising environmental cost it releases prodigious amounts of heattrapping greenhouse gases Prime Cuts How BeefThey collect this heat energy and hold it in the atmosphere, delaying its passage back out of the atmosphere Due in part to the warming effects of the greenhouse gases, the global average temperature is about 15°C (59°F) Without the greenhouse gases the global average temperature would be much colder, about 18°C (0°F)
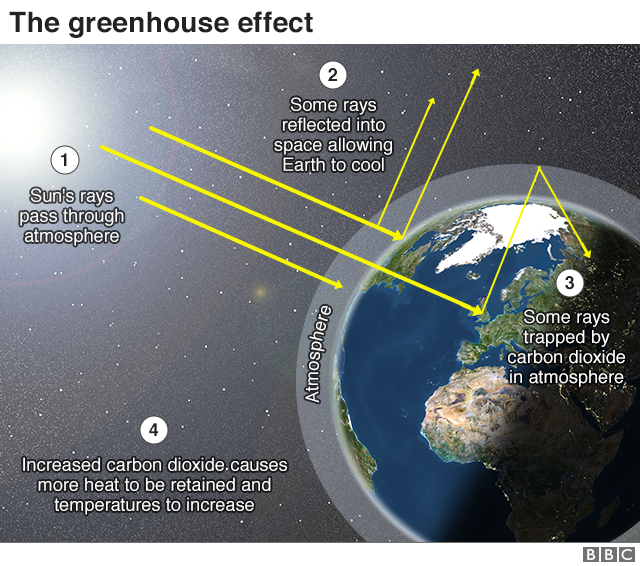



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




Global Warming Schools
Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution, coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphereWater vapor is known to be Earth's most abundant greenhouse gas, but the extent of its contribution to global warming has been debated Using recent NASA satellite data, researchers have estimated more precisely than ever the heattrapping effect of water in the air, validating the role of the gas as a critical component of climate changeThe study report on the Greenhouse gases and their impact on Global warming Without the greenhouse effect the Earth's average global temperature would be much colder and life on Earth as we know it would be impossible Greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide (N2O) and other gases




What Is A Conservatory Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect What Is A Conservatory




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica
The gases present in the atmosphere for example ozone, methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour and chlorofluorocarbons are called greenhouse gases, they absorb some heat thereby restricting the heat to escape our atmosphere These gases add to the heating of the atmosphere and result in global warming The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides"Global warming" refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere "Climate change" refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time – including precipitation, temperature, and wind patterns



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming Earth Reminder
With time running out to try and cap global warming at wellbelow 15 degrees Celsius, every ton of CO2 counts, and knowing how extreme wildfire seasons affect greenhouse gas emissions lets the Greenhouse Gases Effect on Global Warming Animations by Susan Twardy Released on The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward spaceCarbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of years
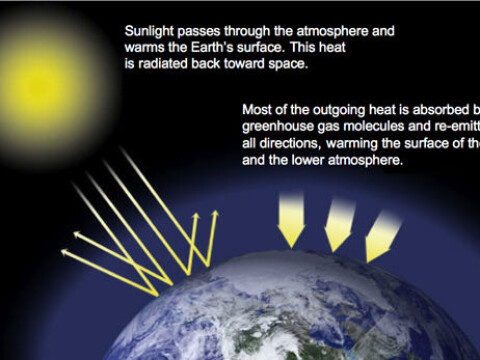



Concern For Global Warming Is Not A New Craze
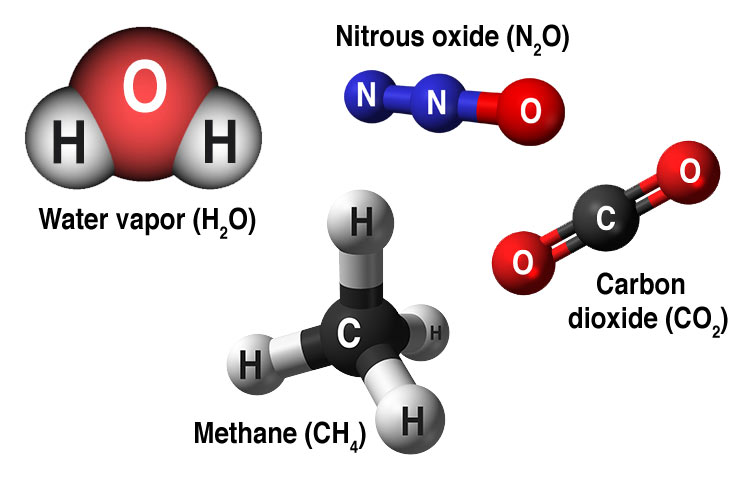



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Greenhouse gases The main driver of climate change is the greenhouse effect Some gases in the Earth's atmosphere act a bit like the glass in a greenhouse, trapping the sun's heat and stopping it from leaking back into space and causing global warmingFor each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long it remains in the atmosphere, on average, and how strongly it absorbs energy Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming EarthThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that maintains the temperature of the earth But when the number of greenhouse gases increases in the atmosphere, it results in a phenomenon known as global warming, which is one of the major problems that the world is facing today We will discuss it in brief in this article below




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
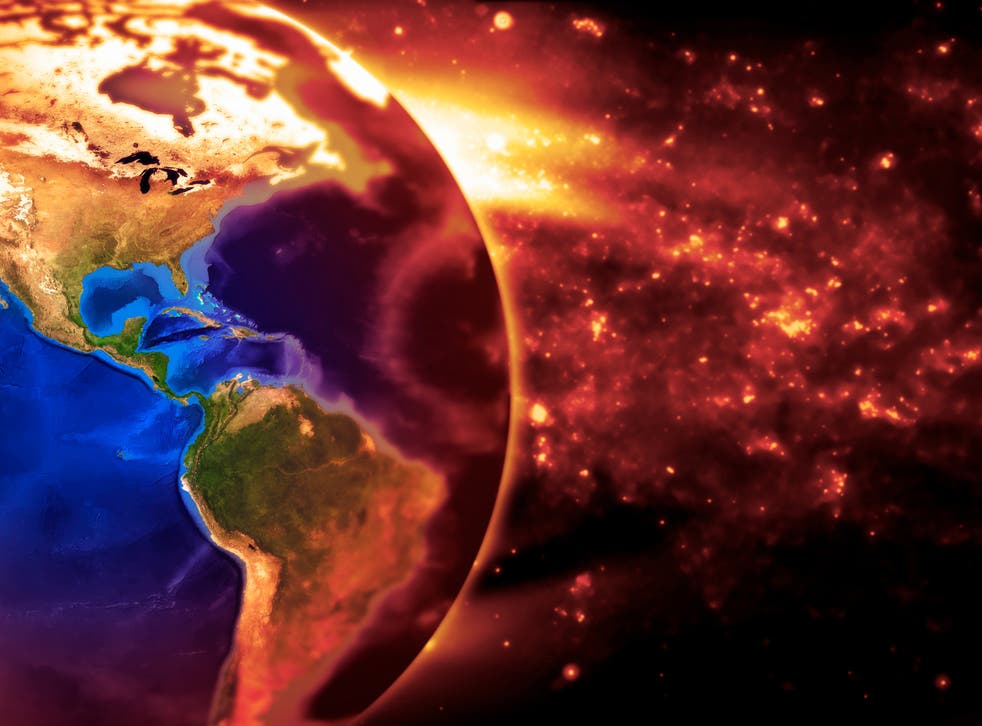
Earth has experienced climate change in the past without help from humanity Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels How Does Today's Warming Compare to Past Climate Change?




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
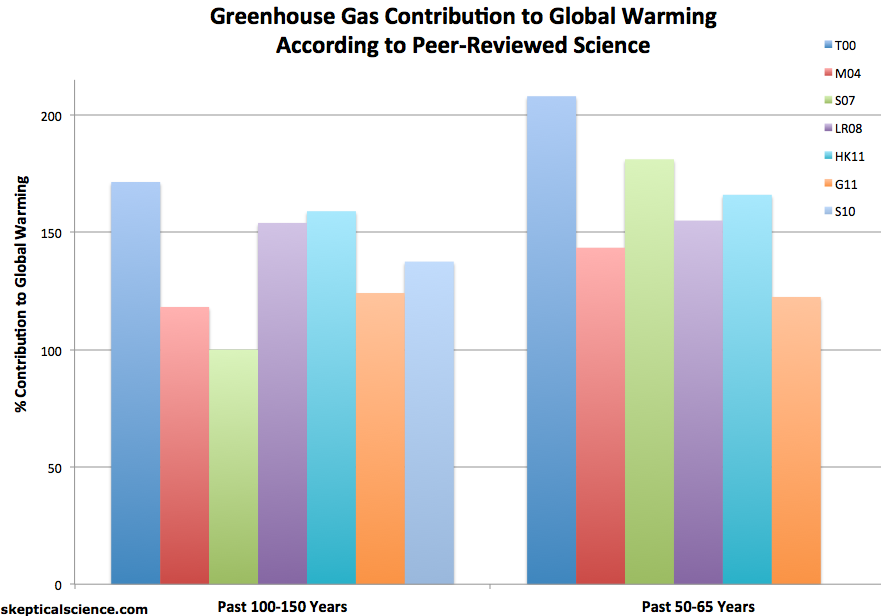



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
Rapid changes in global temperature Increased greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect has contributed to an overall warming of the Earth's climate, leading to a global warming (even though some regions may experience cooling, or wetter weather, while the temperature of the planet on average would rise)Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases Global Warming Climate Change Blog



The Greenhouse Effect Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
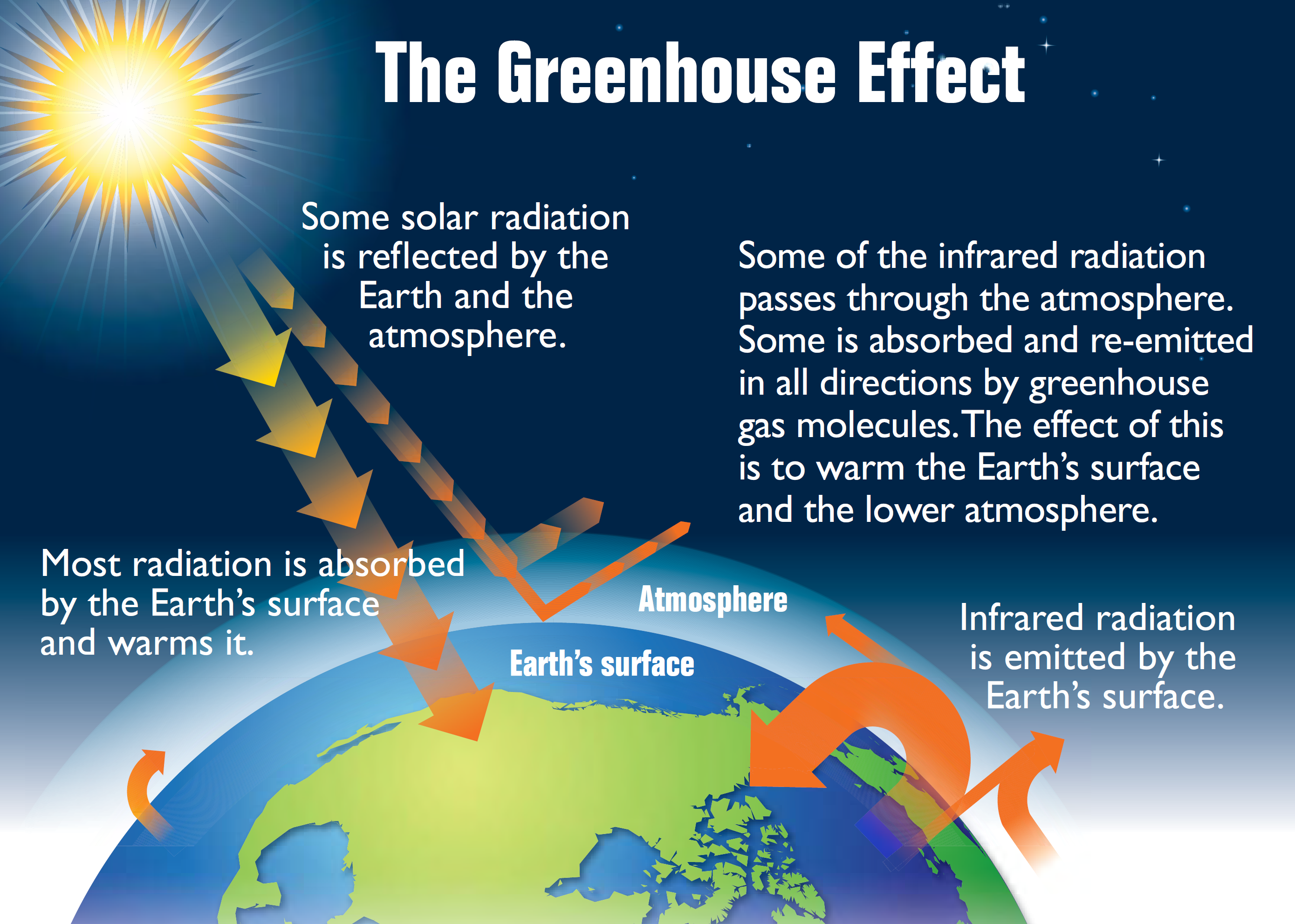



Global Warming Not Just A Blanket In The Long Run It S More Like Tanning Oil Uw News




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




27 Causes Effects Solutions For Global Warming E C



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
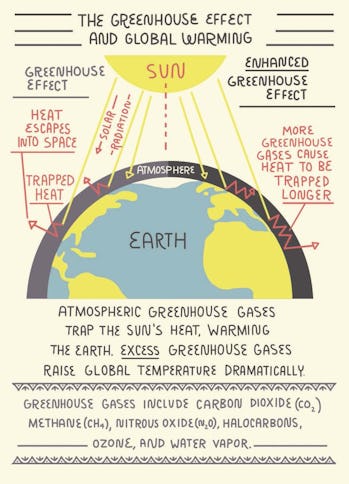



What Is The Greenhouse Effect And How Does It Cause Global Warming




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
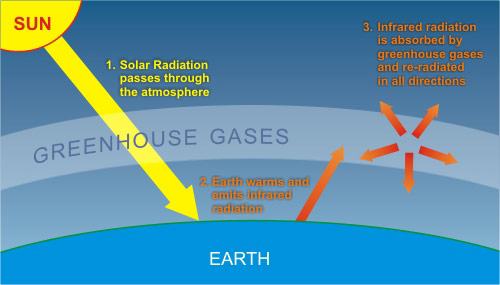



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
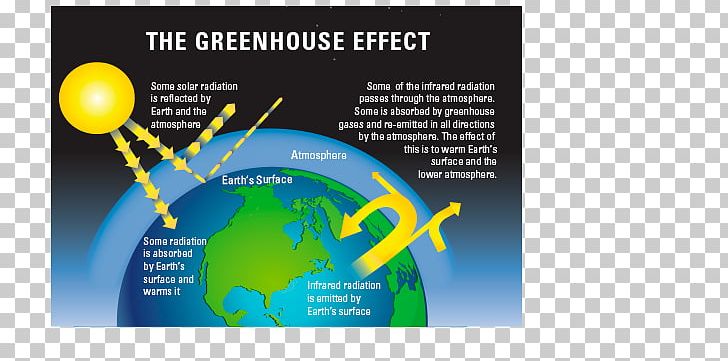



Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Climate Change Evidence And Causes Png Clipart Atmosphere Of Earth
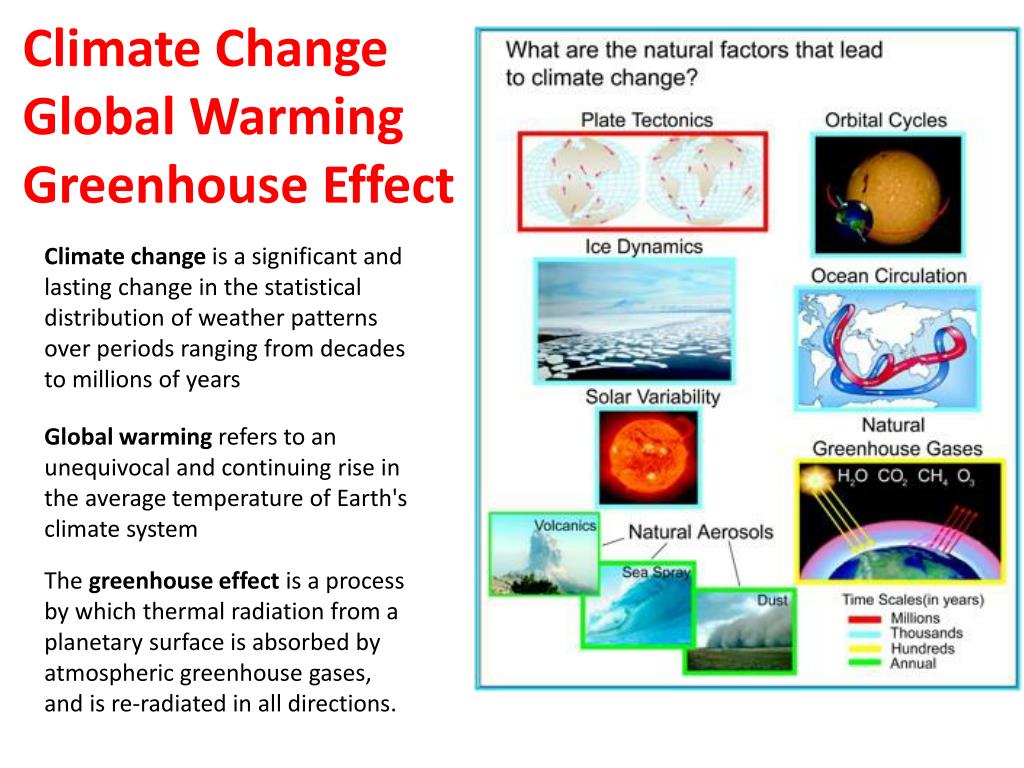



Ppt Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Powerpoint Presentation Id




Greenhouse Gases Worldwide Impacts Global Warming Casper Julie Kerr Ph D Amazon Com Books




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Global Warming Definition Causes Effects Solutions Facts Britannica




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples
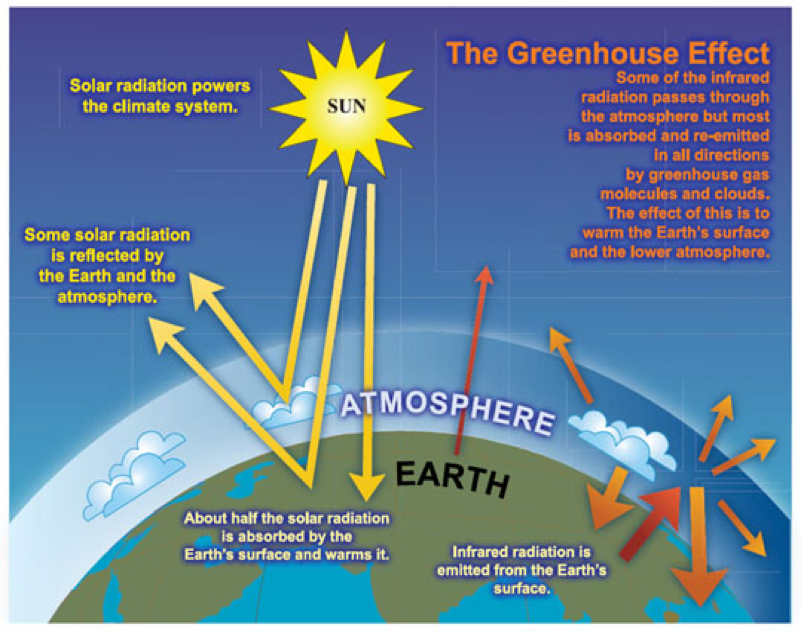



Greenhouse Gas Reduction
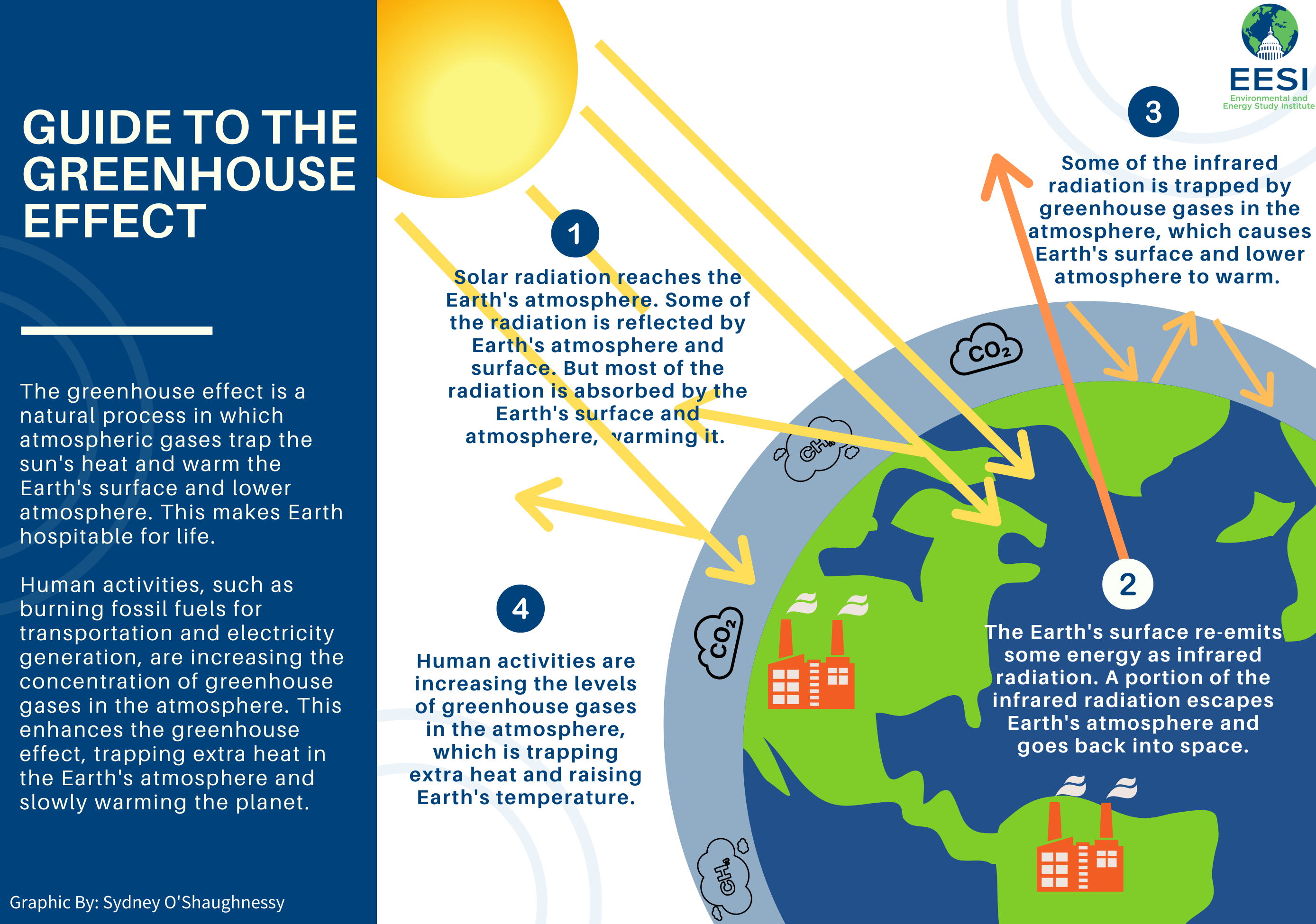



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
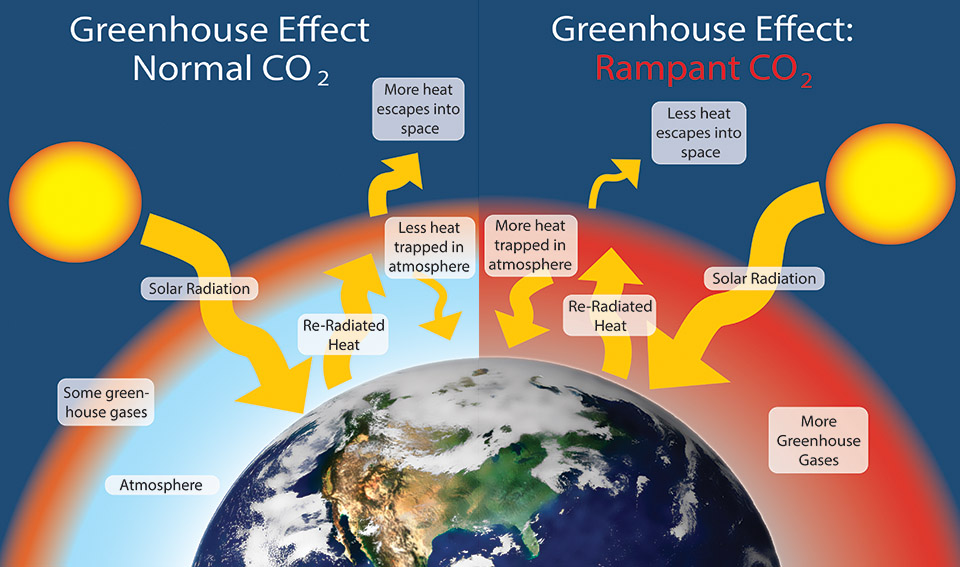



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service
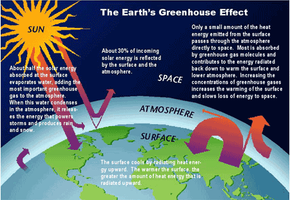



The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks



1




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
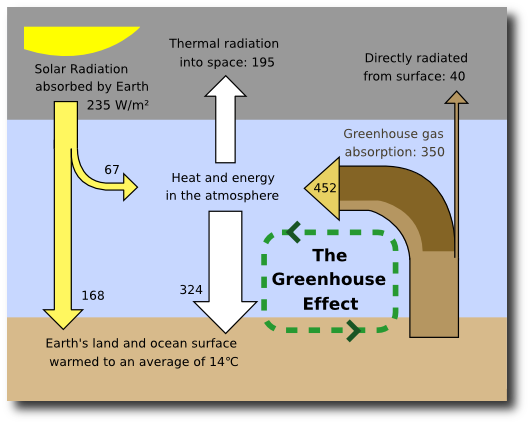



Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction Global Issues




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Change Is In The Air And Water Climate Change And Ocean Health Ocean Health Index




The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Youtube




Difference Between Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
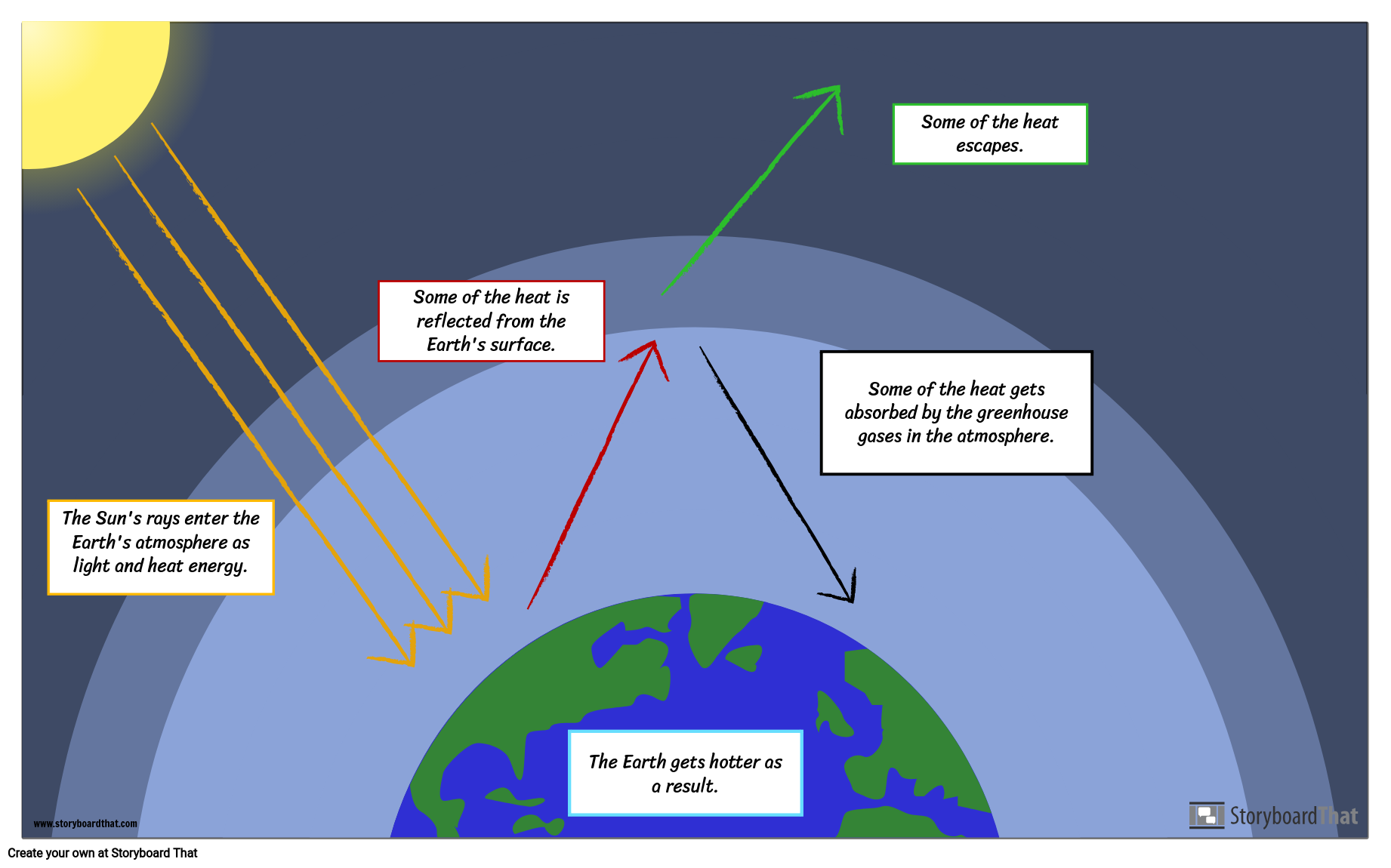



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly



Understanding Climate Change How Greenhouse Gases Warm The Earth Youtube




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
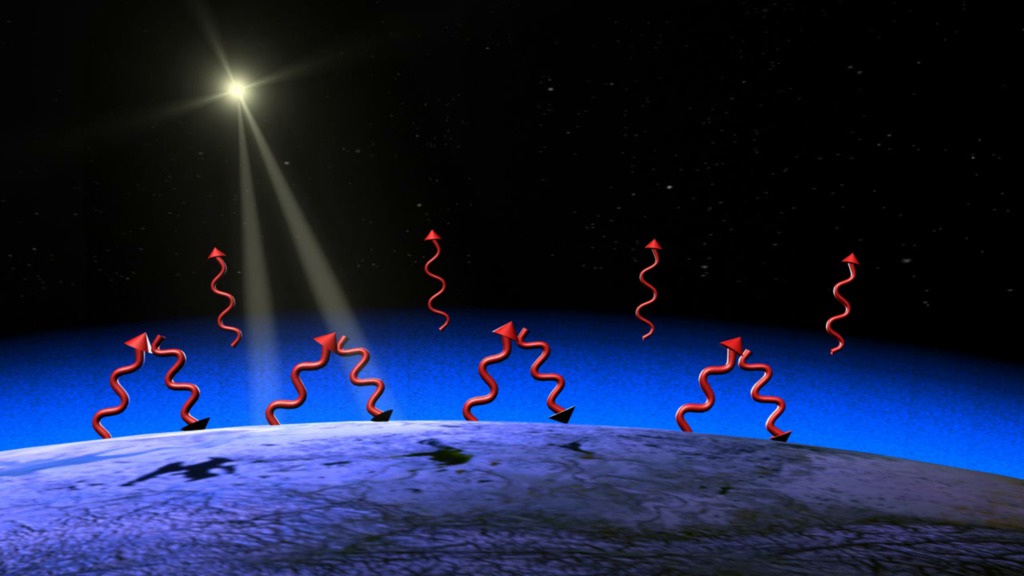



Cilab Greenhouse Gases Effect On Global Warming




Green House Gases Global Warming And Climate Change Public Health Notes
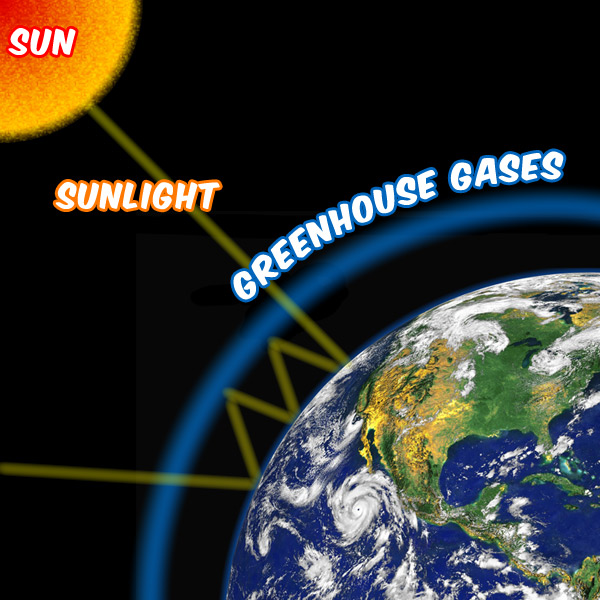



Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Tree House Weather Kids University Of Illinois Extension




Co2 Emission Sources Greenhouse Gases And The Global Warming Effect Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Global Warming Green House Effect Ozone Layer Video For Kids Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Atmospheric Text Globe Png Pngegg




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Infographic The Causes Of Global Warming What S Your Impact




Global Warming Causes And Effects Visual Ly




The Discovery Of Global Warming International Brotherhood Of Boilermakers
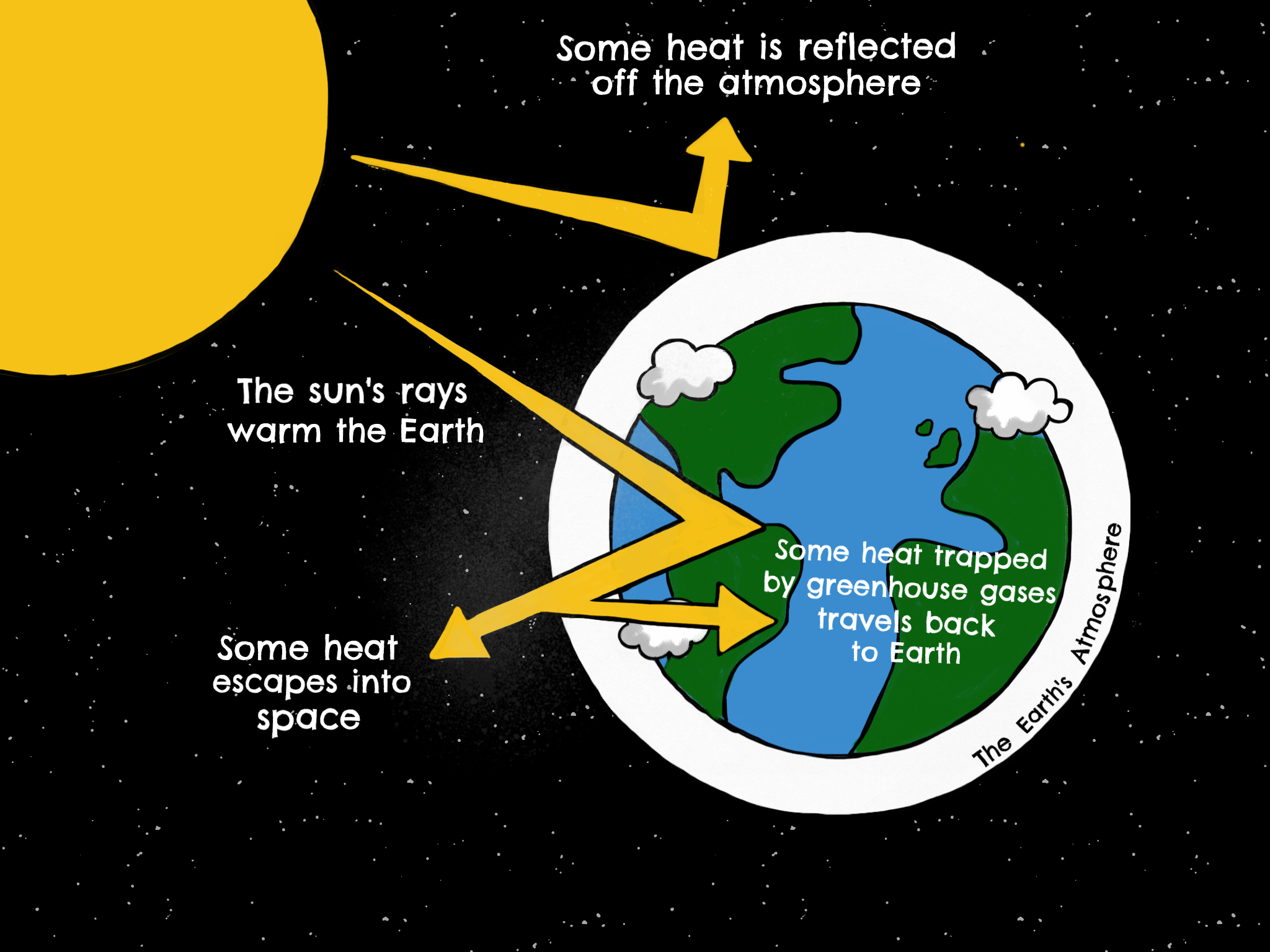



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change




Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Air Pollutant Reductions Could Enhance Global Warming Without Greenhouse Gas Cuts Eurekalert Science News




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Science Classroom Poster Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Global Warming Project




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




What Are Climate Change And Global Warming The Planet App




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




What Is Climate Change Causes And Effects Of Global Warming The Independent



Global Warming
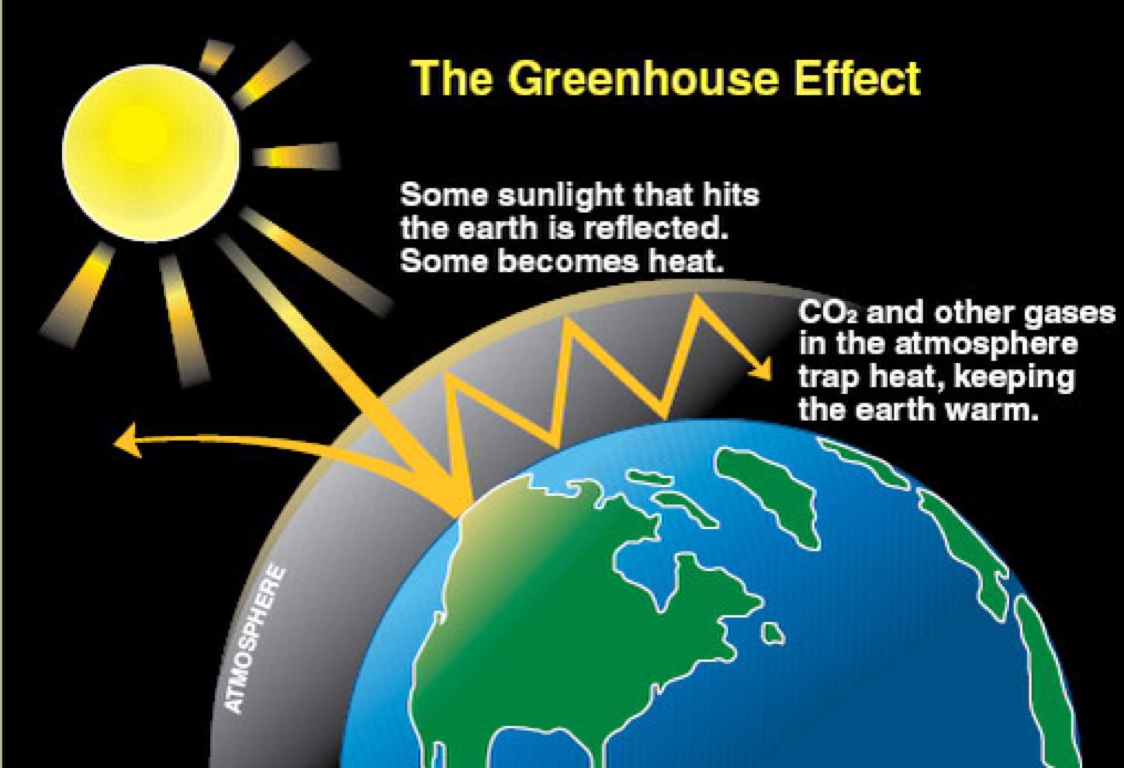



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
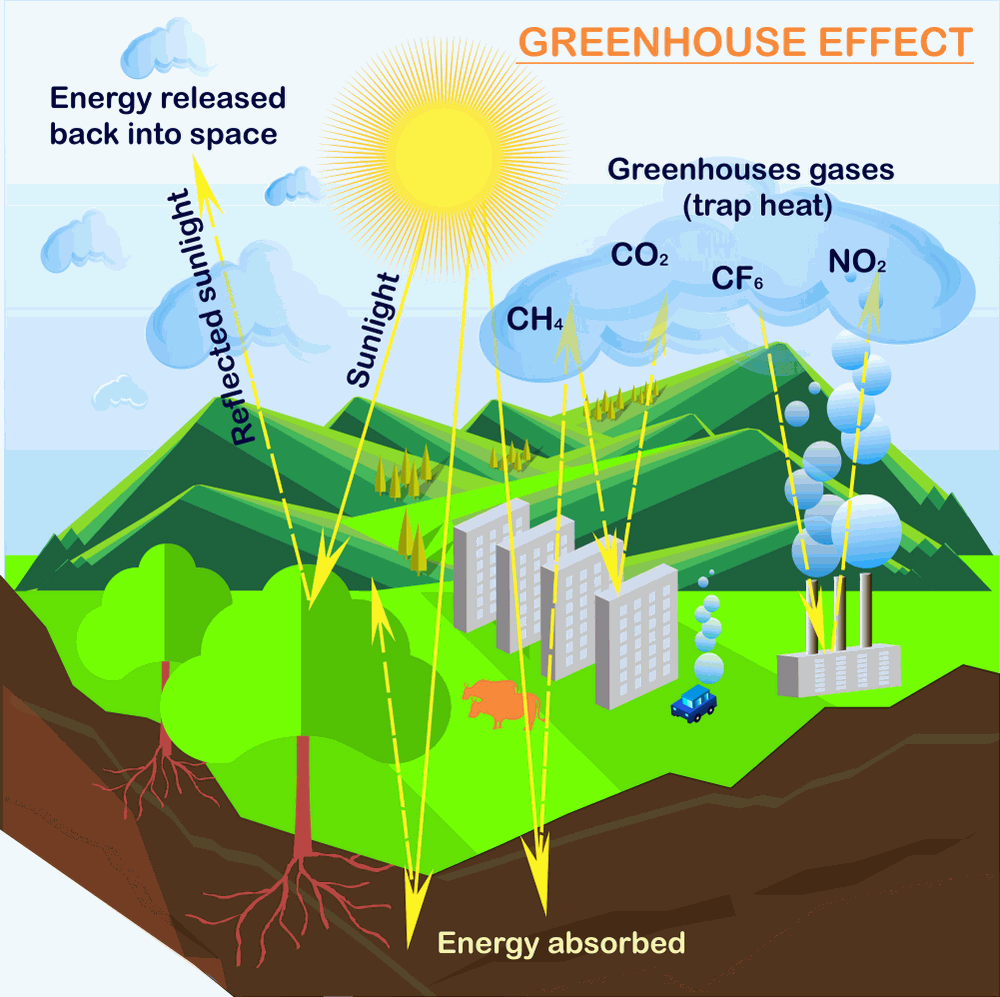



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




What S The Difference Between Global Warming And Climate Change Noaa Climate Gov



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate Change Home Facebook




Natural Gas Effects On Global Warming Co2nsensus




Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That Is A Great Way For Students To Co Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Lesson
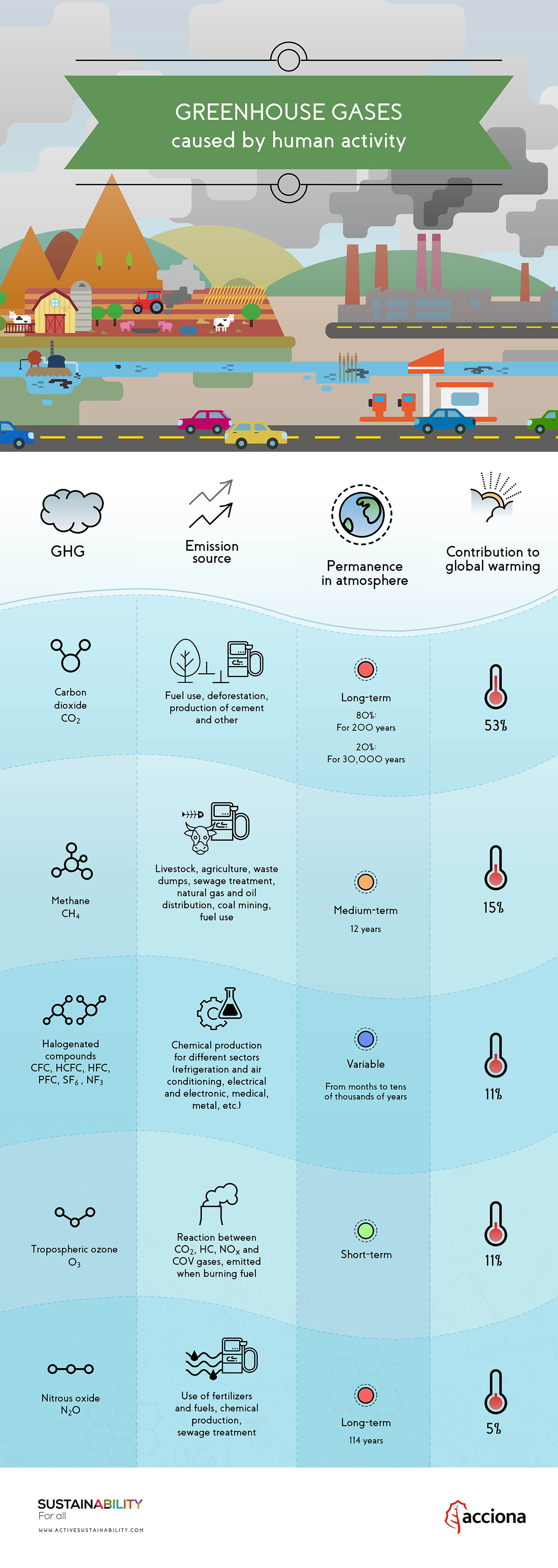



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
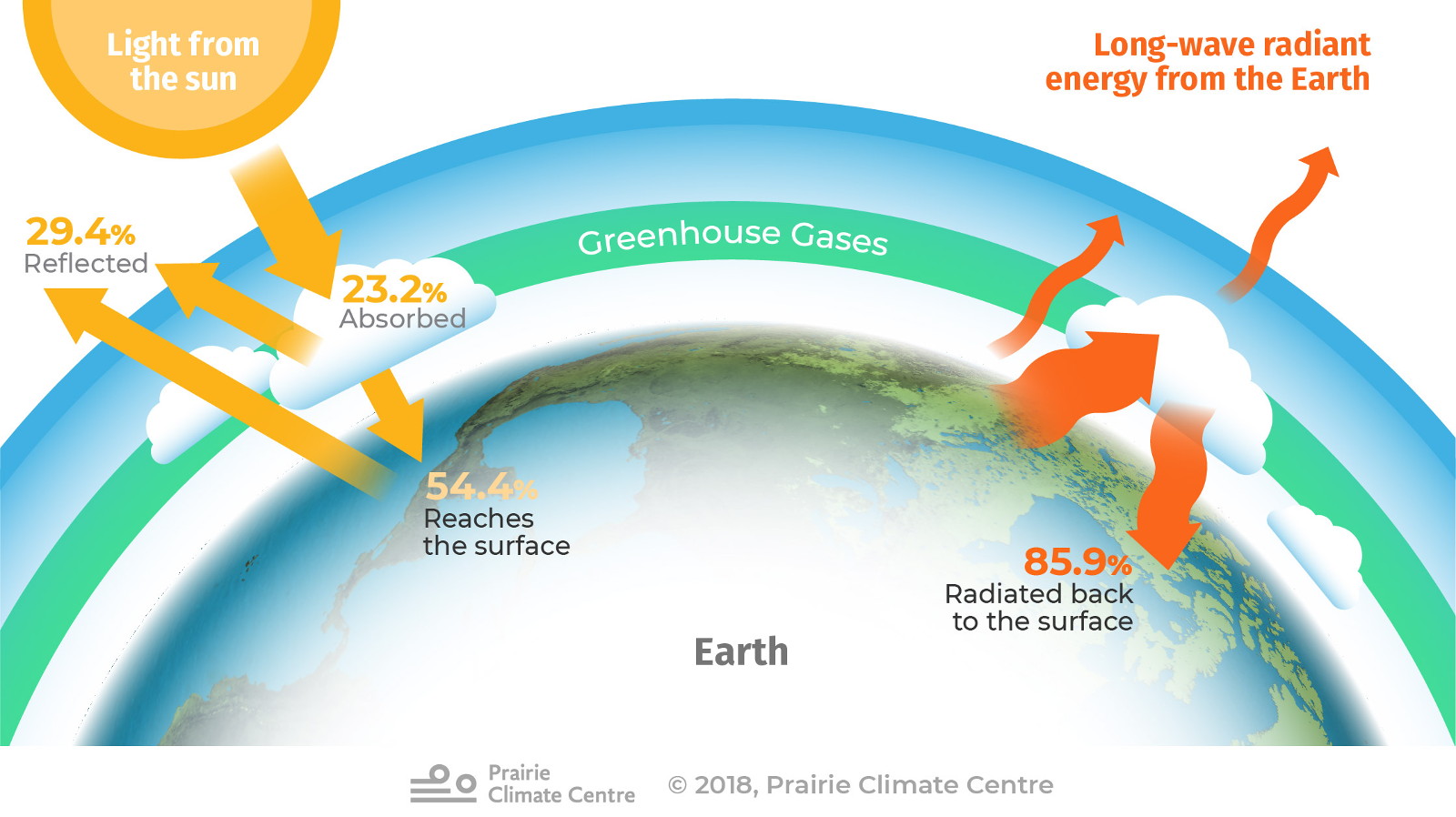



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
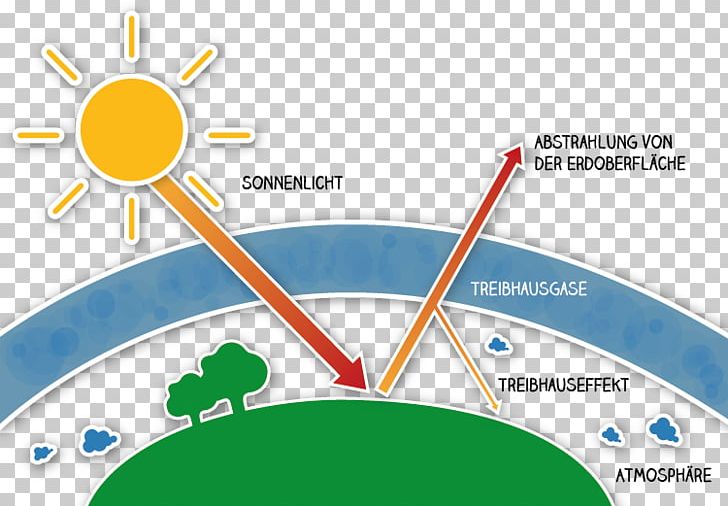



Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Anthropogen Global Warming Png Clipart Angle Area Atmosphere Of Earth



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿